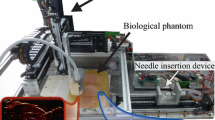
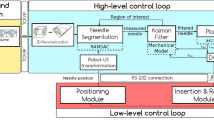
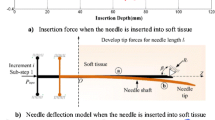
Abstract
The performance of needle-based interventions depends on the accuracy of needle tip positioning. Here, a novel needle steering strategy is proposed that enhances accuracy of needle steering. In our approach the surgeon is in charge of needle insertion to ensure the safety of operation, while the needle tip bevel location is robotically controlled to minimize the targeting error. The system has two main components: (1) a real-time predictor for estimating future needle deflection as it is steered inside soft tissue, and (2) an online motion planner that calculates control decisions and steers the needle toward the target by iterative optimization of the needle deflection predictions. The predictor uses the ultrasound-based curvature information to estimate the needle deflection. Given the specification of anatomical obstacles and a target from preoperative images, the motion planner uses the deflection predictions to estimate control actions, i.e., the depth(s) at which the needle should be rotated to reach the target. Ex-vivo needle insertions are performed with and without obstacle to validate our approach. The results demonstrate the needle steering strategy guides the needle to the targets with a maximum error of 1.22 mm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebar, T. K., A. E. Fletcher, and A. M. Okamura. 3-D ultrasound-guided robotic needle steering in biological tissue. IEEE Tran. Biomed. Eng. 61:2899–2910, 2014.
Choi, A. P. C., and Y. P. Zheng. Estimation of Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of soft tissue from indentation using two different-sized indentors: Finite element analysis of the finite deformation effect. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43:258–264, 2005.
Cowan, N. J., K. Goldberg, G. S. Chirikjian, G. Fichtinger, R. Alterovitz, K. B. Reed, V. Kallem, W. Park, S. Misra, and A. M. Okamura. Surgical Robotics: Systems Applications and Visions. US: Springer, pp. 557–582, 2011.
Delling, D., P. Sanders, D. Schultes, and D. Wagner. Algorithmics of Large and Complex Networks: Design, Analysis, and Simulation. Berlin: Springer, pp. 117–139, 2009.
Goksel, O., E. Dehghan, and S. E. Salcudean. Modeling and simulation of flexible needles. Med. Eng. Phys. 31:1069–1078, 2009.
Jamaluddin, M. F., S. Ghosh, M. Waine, et al. Quantifying iodine-125 placement accuracy in prostate brachytherapy using post-implant transrectal ultrasound images. Brachytherapy 15:S180, 2016.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, R. S. Sloboda, N. Usmani, and M. Tavakoli. Ultrasound-guided model predictive control of needle steering in biological tissue. J. Med. Robot. Res 01:1640007–1640007, 2016.
Khadem, M., C. Rossa, N. Usmani, R. S. Sloboda, and M. Tavakoli. A two-body rigid/flexible model of needle steering dynamics in soft tissue. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron. 21:2352–2364, 2016.
Liao, S. Homotopy analysis method: a new analytic method for nonlinear problems. Appl. Math. Mech. 19:957–962, 1998.
Liao, S. Homotopy Analysis Method in Nonlinear Differential Equations. Berlin: Springer, 2012.
Maghsoudi, A., and M. Jahed. Needle dynamics modelling and control in prostate brachytherapy. IET Control Theory Appl. 6:1671–1681, 2012.
Minhas D. S., J. A. Engh, M. M. Fenske, and C. N. Riviere. Modeling of needle steering via duty-cycled spinning. In: 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), pp. 2756–2759
Misra S., K. B. Reed, A. S. Douglas, K. T. Ramesh, and A. M. Okamura. Needle-tissue interaction forces for bevel-tip steerable needles. In: 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, BioRob, 2008, pp. 224–231
Misra, S., K. B. Reed, B. W. Schafer, K. T. Ramesh, and A. M. Okamura. Mechanics of flexible needles robotically steered through soft tissue. Int. J. Robot. Res. 29:1640–1660, 2010.
Moreira, P., and S. Misra. Biomechanics-based curvature estimation for ultrasound-guided flexible needle steering in biological tissues. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:1716–1726, 2015.
Patil, S., J. Burgner, R. J. Webster, and R. Alterovitz. Needle steering in 3D via rapid replanning. IEEE Trans. Robot. 30:853–864, 2014.
Podder T. K., D. P. Clark, D. Fuller, J. Sherman and et.al. Effects of velocity modulation during surgical needle insertion. In: 27th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE-EMBS. pp. 5766–5770
Reed K. B., V. Kallem, R. Alterovitz, K. Goldberg, A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Integrated planning and image-guided control for planar needle steering. In: 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, BioRob, pp. 819–824
Roesthuis R. J., M. Abayazid and S. Misra. Mechanics-based model for predicting in-plane needle deflection with multiple bends. In: 4th IEEE RAS EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp. 69–74
Rossa C., N. Usmani, R. Sloboda and M. Tavakoli. A hand-held assistant for semi-automated percutaneous needle steering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. pp. 1–1, 2016
Rucker, D. C., J. Das, H. B. Gilbert, P. J. Swaney, M. I. Miga, N. Sarkar, and R. J. Webster. Sliding mode control of steerable needles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 29:1289–1299, 2013.
Swensen, J. P., M. Lin, A. M. Okamura, and N. J. Cowan. Torsional dynamics of steerable needles: modeling and fluoroscopic guidance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61:2707–2717, 2014.
Vrooijink G. J., M. Abayazid, S. Patil, R. Alterovitz, and S. Misra. Needle path planning and steering in a three-dimensional non-static environment using two-dimensional ultrasound images. Int. J. Robot. Res., 2014
Waine M., C. Rossa, R. Sloboda, N. Usmani and M. Tavakoli. 3D needle shape estimation in TRUS-guided prostate brachytherapy using 2D ultrasound images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf., pp. 1–1, 2015
Webster R., N. Cowan, G. Chirikjian, and A. Okamura. Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. In: Experimental Robotics, Vol. IX. Berlin: Springer, 2006, pp. 35–44
Yan, K. G., T. Podder, Y. Yu, T. I. Liu, C. W. S. Cheng, and W. S. Ng. Flexible needle-tissue interaction modeling with depth-varying mean parameter: preliminary study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56:255–262, 2009.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada under grant CHRP 446520, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) under grant CPG 127768 and the Alberta Innovates - Health Solutions (AIHS) under grant CRIO 201201232. The authors would like to thank Dr. Muhammad Faisal Jamaluddin who worked closely with us in conducting the evaluation experiments and helping to analyze our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Xiaoxiang Zheng oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khadem, M., Rossa, C., Usmani, N. et al. Semi-Automated Needle Steering in Biological Tissue Using an Ultrasound-Based Deflection Predictor. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 924–938 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1736-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1736-x